Checkpoints
Create a Cloud Storage Bucket
/ 50
Create a dataset
/ 50
Classify Images of Clouds in the Cloud with AutoML Images
GSP223
Overview
AutoML helps developers with limited ML expertise train high quality image recognition models. Once you upload images to the AutoML UI, you can generate predictions against a pre-trained model via an easy to use REST API. In this lab, you upload images to Cloud Storage and use them to generate predictions from a pre-trained AutoML model.
Objectives
In this lab, will:
- Upload a labeled dataset to Cloud Storage and connect it to AutoML with a CSV label file.
- Generate predictions against a pre-trained model.
Setup and requirements
Before you click the Start Lab button
Read these instructions. Labs are timed and you cannot pause them. The timer, which starts when you click Start Lab, shows how long Google Cloud resources will be made available to you.
This hands-on lab lets you do the lab activities yourself in a real cloud environment, not in a simulation or demo environment. It does so by giving you new, temporary credentials that you use to sign in and access Google Cloud for the duration of the lab.
To complete this lab, you need:
- Access to a standard internet browser (Chrome browser recommended).
- Time to complete the lab---remember, once you start, you cannot pause a lab.
How to start your lab and sign in to the Google Cloud console
-
Click the Start Lab button. If you need to pay for the lab, a pop-up opens for you to select your payment method. On the left is the Lab Details panel with the following:
- The Open Google Cloud console button
- Time remaining
- The temporary credentials that you must use for this lab
- Other information, if needed, to step through this lab
-
Click Open Google Cloud console (or right-click and select Open Link in Incognito Window if you are running the Chrome browser).
The lab spins up resources, and then opens another tab that shows the Sign in page.
Tip: Arrange the tabs in separate windows, side-by-side.
Note: If you see the Choose an account dialog, click Use Another Account. -
If necessary, copy the Username below and paste it into the Sign in dialog.
{{{user_0.username | "Username"}}} You can also find the Username in the Lab Details panel.
-
Click Next.
-
Copy the Password below and paste it into the Welcome dialog.
{{{user_0.password | "Password"}}} You can also find the Password in the Lab Details panel.
-
Click Next.
Important: You must use the credentials the lab provides you. Do not use your Google Cloud account credentials. Note: Using your own Google Cloud account for this lab may incur extra charges. -
Click through the subsequent pages:
- Accept the terms and conditions.
- Do not add recovery options or two-factor authentication (because this is a temporary account).
- Do not sign up for free trials.
After a few moments, the Google Cloud console opens in this tab.

Activate Cloud Shell
Cloud Shell is a virtual machine that is loaded with development tools. It offers a persistent 5GB home directory and runs on the Google Cloud. Cloud Shell provides command-line access to your Google Cloud resources.
- Click Activate Cloud Shell
at the top of the Google Cloud console.
When you are connected, you are already authenticated, and the project is set to your Project_ID,
gcloud is the command-line tool for Google Cloud. It comes pre-installed on Cloud Shell and supports tab-completion.
- (Optional) You can list the active account name with this command:
- Click Authorize.
Output:
- (Optional) You can list the project ID with this command:
Output:
gcloud, in Google Cloud, refer to the gcloud CLI overview guide.
Task 1. Set up AutoML
AutoML provides an interface for all the steps in training an image classification model and generating predictions on it. Start by enabling the Cloud AutoML API.
-
From the Navigation menu, select APIs & Services > Library.
-
In the search bar type in "Cloud AutoML".
-
Observe the Cloud AutoML API is in the Enable state.
-
In a new browser, open the AutoML UI.
Create storage bucket
- Now create a storage bucket by running the following:
- In the Google Cloud console, open the Navigation menu and click on Cloud Storage to see it.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Task 2. Upload training images to Cloud Storage
In order to train a model to classify images of clouds, you need to provide labelled training data so the model can develop an understanding of the image features associated with different types of clouds. In this example your model will learn to classify three different types of clouds: cirrus, cumulus, and cumulonimbus. To use AutoML you need to put your training images in Cloud Storage.
- Before adding the cloud images, create an environment variable with the name of your bucket.
Run the following command in Cloud Shell:
The training images are publicly available in a Cloud Storage bucket.
- Use the
gsutilcommand line utility for Cloud Storage to copy the training images into your bucket:
- When the images finish copying, click the Refresh button at the top of the Storage browser, then click on your bucket name. You should see 3 folders of photos for each of the 3 different cloud types to be classified.
If you click on the individual image files in each folder you can see the photos you'll be using to train your model for each type of cloud.
Task 3. Create a dataset
Now that your training data is in Cloud Storage, you need a way for AutoML to access it. You'll create a CSV file where each row contains a URL to a training image and the associated label for that image. This CSV file has been created for you; you just need to update it with your bucket name.
- Run the following command to copy the file to your Cloud Shell instance:
- Then update the CSV with the files in your project:
- Now upload this file to your Cloud Storage bucket:
-
Once that command completes, click the Refresh button at the top of the Storage browser. Confirm that you see the
data.csvfile in your bucket. -
Open the Vertex AI Dataset tab. Your page should now resemble the following:
-
At the top of the console, click + Create.
-
Type "clouds" for the Dataset name.
-
Select Image classification (Single-label).
-
Click Create.
-
Choose Select import files from Cloud Storage and add the file name to the URL for the file you just uploaded -
your-bucket-name/data.csv
An easy way to get this link is to go back to the Cloud Console, click on the data.csv file and then go to the URI field.
- Click Continue.
It will take 2 - 5 minutes for your images to import. Once the import has completed, you'll be brought to a page with all the images in your dataset.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Task 4. Inspect images
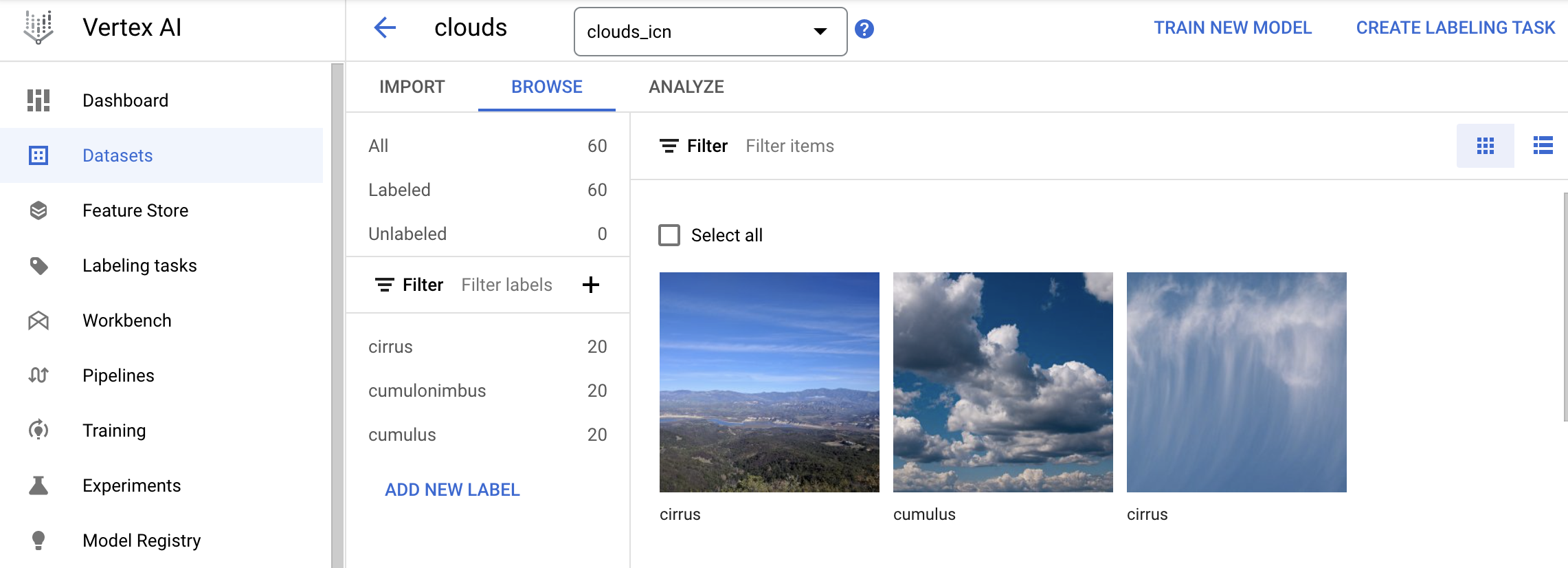
After the import completes, you will be redirected to Browse tab to see the images you uploaded.
Try filtering by different labels in the left menu (i.e. click cumulus) to review the training images:
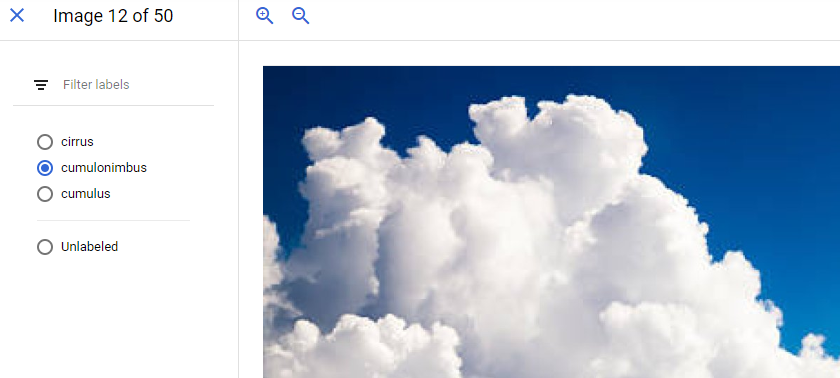
If any images are labeled incorrectly you can click on the image to switch the label:
Given that model training requires significant time, you will utilize a pre-trained model for this lab. In the following section, you will use this model to generate predictions on the images you uploaded in the previous section.
Task 5. Generate predictions
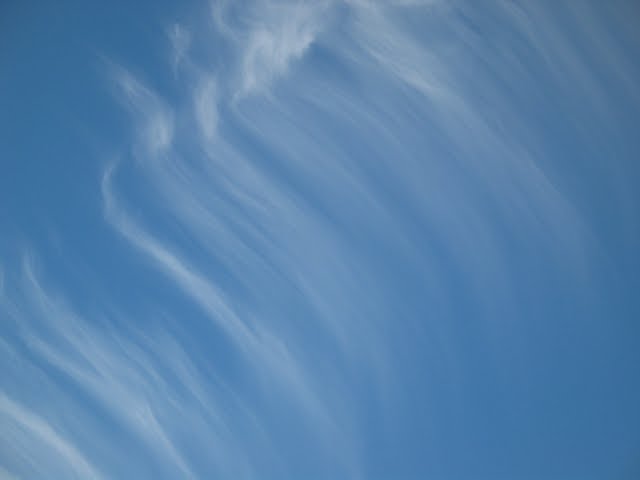
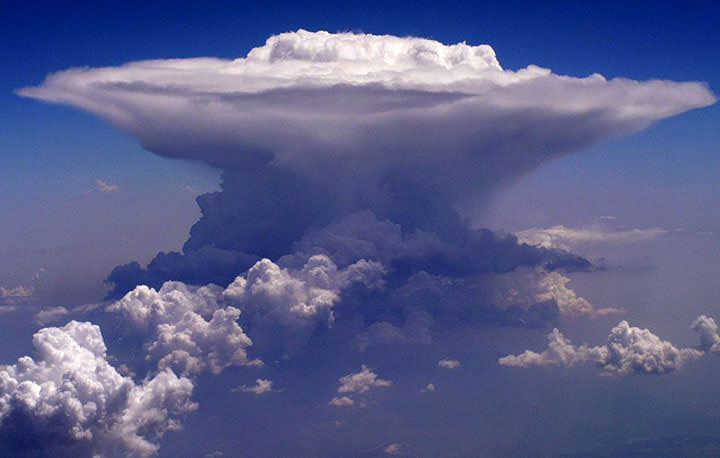
There are a few ways to generate predictions. In this lab, you'll use the UI to upload images and see how your model does classifying these two images (the first is a cirrus cloud, the second is a cumulonimbus).
-
Return to the Cloud Shell terminal.
-
Download these images to your local machine.
- View the example file
CLOUD1-JSON:
Example Output:
- Copy the Endpoint value to an environment variable:
- Enter the following command to request a prediction:
Expected Output:
Task 6. Pop Quiz
Test your understanding of AutoML by completing the short quiz on the topics covered in this lab. Use the knowledge you have gained in the lab to generate predictions.
Check if the model can predict the type of cloud in the image:
- Set
CLOUD1-JSONas the input file.
- Enter the following command to request a prediction:
Check if the model can predict the type of cloud in the image:
- Set
CLOUD2-JSONas the input file.
- Enter the following command to request a prediction:
Congratulations!
Congratulations! In this lab, you learned how to use AutoML to classify images of clouds. You first uploaded training images to Cloud Storage and created a CSV for AutoML to find these images. Then you generated predictions on new cloud images using a pre-trained model.
Next steps / Learn more
- Watch Introducing Cloud AutoML
- Learn more about how AutoML works by listening to the Google Cloud Podcast episode
- Read the announcement blog post
- Learn how to perform each step with the API, see Introduction to Vertex
Google Cloud training and certification
...helps you make the most of Google Cloud technologies. Our classes include technical skills and best practices to help you get up to speed quickly and continue your learning journey. We offer fundamental to advanced level training, with on-demand, live, and virtual options to suit your busy schedule. Certifications help you validate and prove your skill and expertise in Google Cloud technologies.
Manual Last Updated December 27, 2023
Lab Last Tested December 27, 2023
Copyright 2024 Google LLC All rights reserved. Google and the Google logo are trademarks of Google LLC. All other company and product names may be trademarks of the respective companies with which they are associated.