Checkpoints
Setup Cloud Storage bucket
/ 15
Add Cloud Data Fusion API Service Agent role to service account
/ 15
Get Sensitive Data Protection permissions
/ 15
Create a custom template
/ 20
Redact another data type
/ 15
Deploy and run the pipeline
/ 20
Redacting Confidential Data within your Pipelines in Cloud Data Fusion
- GSP811
- Overview
- Setup and requirements
- Task 1. Set up the Cloud Storage bucket
- Task 2. Add the necessary permissions for your Cloud Data Fusion instance
- Task 3. Get Sensitive Data Protection permissions
- Task 4. Navigate to the Cloud Data Fusion UI
- Task 5. Create the pipeline
- Task 6. Redact sensitive data
- Task 7. Deploy the Sensitive Data Protection plugin
- Task 8. Create a custom template
- Task 9. Apply the Redact transform
- Task 10. Store the output data
- Task 11. Run the pipeline in preview mode
- Task 12. Redact another data type
- Task 13. Deploy and run the pipeline
- Task 14. View the results
- Congratulations!
GSP811
Overview
In this lab, you wil learn how to use the Sensitive Data Protection plugin for Cloud Fusion to redact sensitive data.
Consider the following scenario, in which some sensitive customer information needs to be redacted.
Scenario: Your support team documents the details of each support case they handle in a support ticket. All of the information in the support tickets is pulled into a CSV file. The support technicians are not supposed to document any customer information that's considered sensitive, but sometimes they mistakenly do so. You notice that in the CSV file some customers' phone numbers appear.
You want to go through the CSV file and hide all phone numbers. You create a Cloud Data Fusion pipeline that redacts the sensitive customer data by using the Sensitive Data Protection plugin.
You will create a pipeline that does the following:
- Redacts customer phone numbers and emails by masking them with the # character.
- Stores the masked sensitive data and the non-sensitive data in a Cloud Storage.
Objectives
In this lab, you will learn how to do the following:
- Connect Cloud Data Fusion to a Cloud Storage source.
- Deploy the Sensitive Data Protection plugin.
- Create a custom Sensitive Data Protection template.
- Use the Redact transform plugin to mask sensitive customer data.
- Write the output data to Cloud Storage.
Setup and requirements
For each lab, you get a new Google Cloud project and set of resources for a fixed time at no cost.
-
Sign in to Google Cloud Skills Boost using an incognito window.
-
Note the lab's access time (for example, 02:00:00), and make sure you can finish within that time.
There is no pause feature. You can restart if needed, but you have to start at the beginning. -
When ready, click Start lab.
Note: Once you click Start lab, it will take about 15 - 20 minutes for the lab to provision necessary resources and create a Data Fusion instance. During that time, you can read through the steps below to get familiar with the goals of the lab. When you see lab credentials (Username and Password) in the left panel, the instance is created and you can continue logging into the console. -
Note your lab credentials (Username and Password). You will use them to sign in to the Google Cloud console.
-
Click Open Google console.
-
Click Use another account and copy/paste credentials for this lab into the prompts.
If you use other credentials, you'll receive errors or incur charges. -
Accept the terms and skip the recovery resource page.
Log in to Google Cloud Console
- Using the browser tab or window you are using for this lab session, copy the Username from the Connection Details panel and click the Open Google Console button.
- Paste in the Username, and then the Password as prompted.
- Click Next.
- Accept the terms and conditions.
Since this is a temporary account, which will last only as long as this lab:
- Do not add recovery options
- Do not sign up for free trials
- Once the console opens, view the list of services by clicking the Navigation menu (
) at the top-left.
Activate Cloud Shell
Cloud Shell is a virtual machine that contains development tools. It offers a persistent 5-GB home directory and runs on Google Cloud. Cloud Shell provides command-line access to your Google Cloud resources. gcloud is the command-line tool for Google Cloud. It comes pre-installed on Cloud Shell and supports tab completion.
-
Click the Activate Cloud Shell button (
) at the top right of the console.
-
Click Continue.
It takes a few moments to provision and connect to the environment. When you are connected, you are also authenticated, and the project is set to your PROJECT_ID.
Sample commands
- List the active account name:
(Output)
(Example output)
- List the project ID:
(Output)
(Example output)
Check project permissions
Before you begin working on Google Cloud, you must ensure that your project has the correct permissions within Identity and Access Management (IAM).
-
In the Google Cloud console, on the Navigation menu (
), click IAM & Admin > IAM.
-
Confirm that the default compute Service Account
{project-number}-compute@developer.gserviceaccount.comis present and has theeditorrole assigned. The account prefix is the project number, which you can find on Navigation menu > Cloud overview.
If the account is not present in IAM or does not have the editor role, follow the steps below to assign the required role.
-
In the Google Cloud console, on the Navigation menu, click Cloud overview.
-
From the Project info card, copy the Project number.
-
On the Navigation menu, click IAM & Admin > IAM.
-
At the top of the IAM page, click Add.
-
For New principals, type:
Replace {project-number} with your project number.
-
For Select a role, select Basic (or Project) > Editor.
-
Click Save.
Task 1. Set up the Cloud Storage bucket
You will create a Cloud Storage bucket in your project so your pipeline can store output data.
-
In Cloud Shell, execute the following commands to create a new bucket:
export BUCKET=$GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT gcloud storage buckets create gs://$BUCKET
The created bucket name has the same name as your Project ID.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Task 2. Add the necessary permissions for your Cloud Data Fusion instance
- In the Cloud Console, from the Navigation menu select Data Fusion > Instances. You should see a Cloud Data Fusion instance already set up and ready for use.
Next, you will grant permissions to the service account associated with the instance, using the following steps.
-
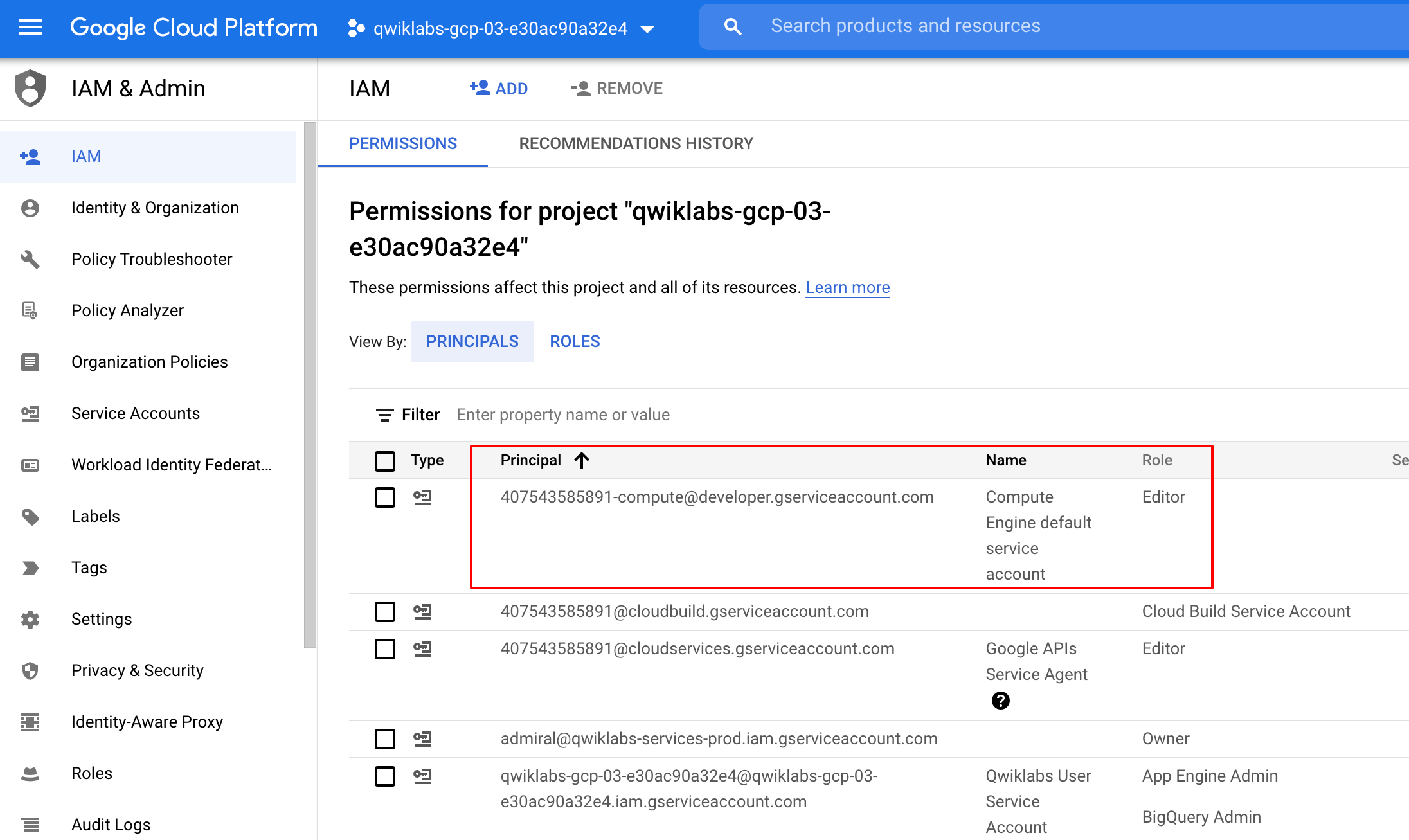
From the Google Cloud console, navigate to the IAM & Admin > IAM.
-
Confirm that the Compute Engine Default Service Account
{project-number}-compute@developer.gserviceaccount.comis present, copy the Service Account to your clipboard. -
On the IAM Permissions page, click +Grant Access.
-
In the New principals field paste the service account.
-
Click into the Select a role field and start typing "Cloud Data Fusion API Service Agent", then select it.
-
Click Save.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Grant service account user permission
-
In the console, on the Navigation menu, click IAM & admin > IAM.
-
Select the Include Google-provided role grants checkbox.
-
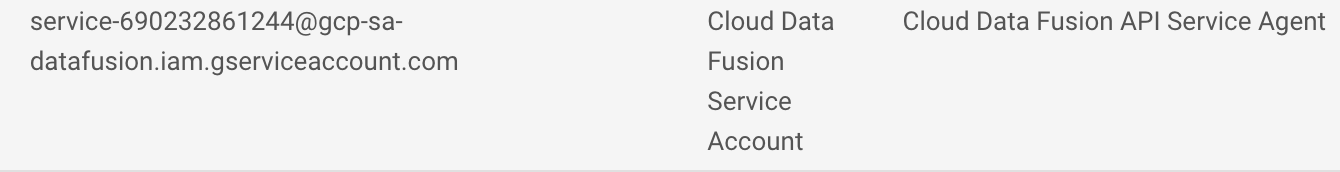
Scroll down the list to find the Google-managed Cloud Data Fusion service account that looks like
service-{project-number}@gcp-sa-datafusion.iam.gserviceaccount.comand then copy the service account name to your clipboard.
-
Next, navigate to the IAM & admin > Service Accounts.
-
Click on the default compute engine account that looks like
{project-number}-compute@developer.gserviceaccount.com, and select the Permissions tab on the top navigation. -
Click on the Grant Access button.
-
In the New Principals field, paste the service account you copied earlier.
-
In the Role dropdown menu, select Service Account User.
-
Click Save.
Task 3. Get Sensitive Data Protection permissions
-
In the Cloud Console, go to Navigation menu > IAM.
-
At the top right of the Permissions table, look for the Include Google-provided role grants checkbox and click it.
- In the permissions table, in the Principal column, find the service account that matches the format
service-project-number@gcp-sa-datafusion.iam.gserviceaccount.com.
-
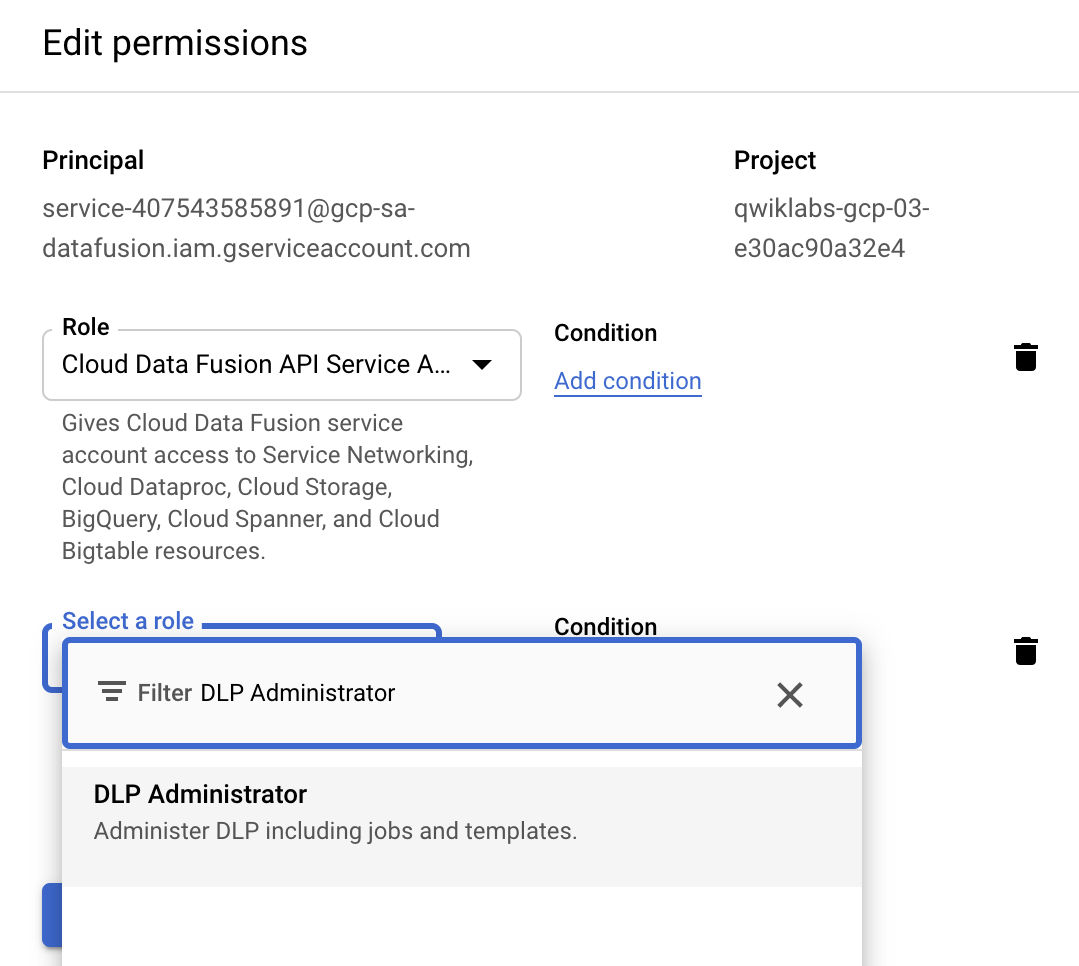
Click the Edit button to the right of the service account.
-
Click Add Another Role.
-
Click the dropdown that appears.
-
Use the search bar to search and then select DLP Administrator.
-
Click Save.
-
Check that DLP Administrator appears in the Role column.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Task 4. Navigate to the Cloud Data Fusion UI
-
In the Console, return to Navigation menu > Data Fusion, then click the View Instance link next to your Data Fusion instance. Select your lab credentials to sign in, if required. If prompted to take a tour of the service click on No, Thanks. You should now be in the Cloud Data Fusion UI.
-
In the Cloud Data Fusion UI, click the Navigation menu on the top left and navigate to the Studio page.
Next, you will create a pipeline.
Task 5. Create the pipeline
The pipeline that you will build does the following: * Reads the input data using the Cloud Storage source plugin. * Deploys the Sensitive Data Protection plugin from the Hub and applys the Redact transform plugin. * Writes the output data using a Cloud Storage sink plugin.
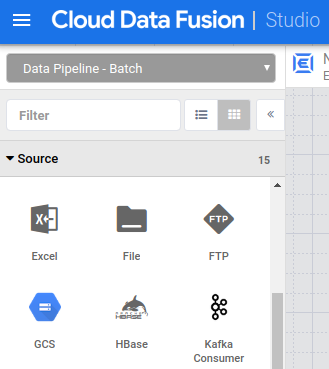
- In the left panel of your Studio page, under the Source menu, click the Google Cloud Storage (GCS) plugin.
-
Hold the pointer over the GCS node that appears and click Properties.
-
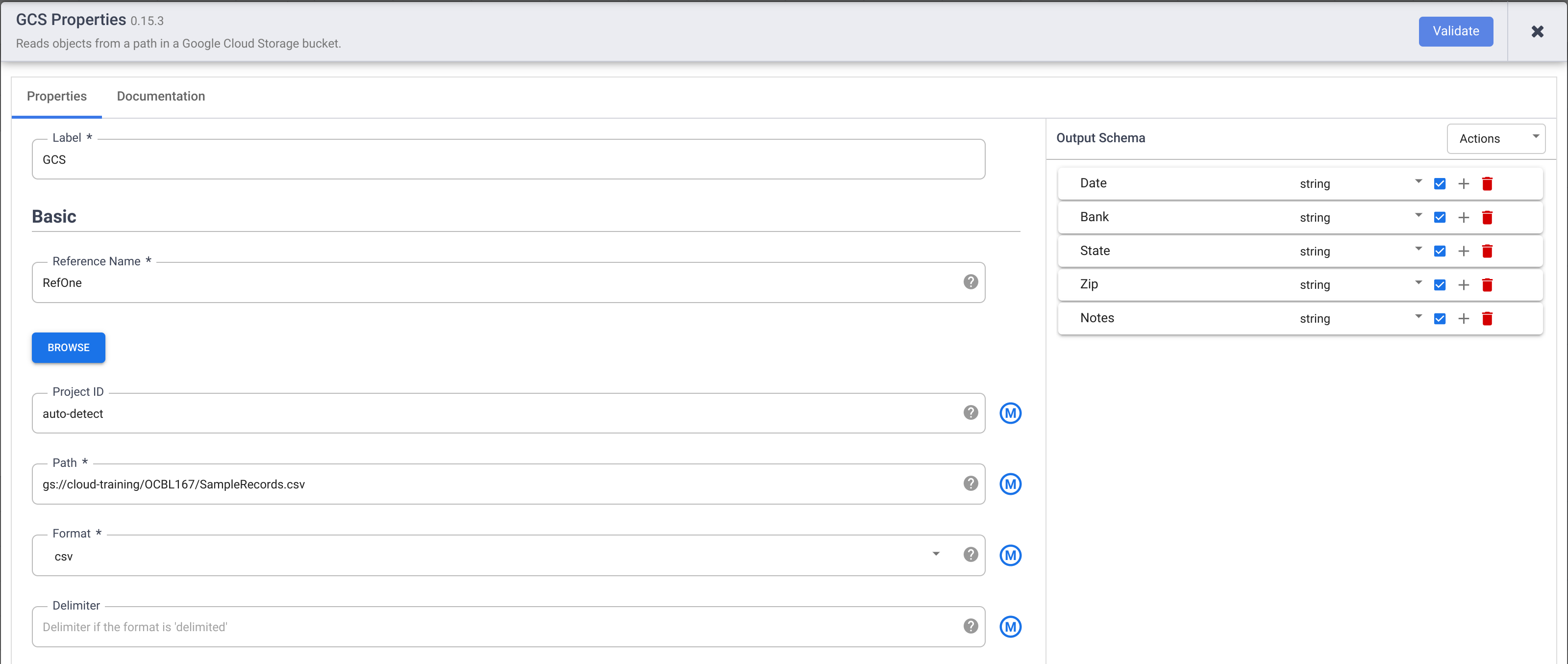
Under Reference Name, enter a reference name.
-
This lab uses the input dataset SampleRecords.csv, provided in a publicly-available Cloud Storage bucket. Under Path, enter
gs://cloud-training/OCBL167/SampleRecords.csv -
Under Format, select csv.
-
Under Output Schema, under Field name, enter the following by clicking the + button for each data type. Remove all existing data types, if any.
- Date
- Bank
- State
- Zip
- Notes
-
Make sure all data types are of type string. To change the type, click Type and select String from the dropdown.
-
Select the checkbox for each data type. This ensures that the pipeline doesn't fail when it encounters a null (empty) value.
-
Click Validate to ensure that there are no errors.
-
Click the X button in the upper-right corner of the dialog box.
Task 6. Redact sensitive data
The Redact transform plugin identifies sensitive records in your input stream of data and applies transformations that you define to those records. A record of data is considered sensitive if it matches pre-defined Sensitive Data Protection filters you choose or a custom template you define.
For this lab, you want to redact customer phone numbers that some support technicians on your team accidentally took note of. They entered the sensitive information in the Notes section of the support tickets, which appears as the Notes column in the CSV file. You create a custom Sensitive Data Protection inspection template, and then provide the template ID in the properties menu of the Redact transform plugin.
Task 7. Deploy the Sensitive Data Protection plugin
-
In the Cloud Data Fusion UI, click Hub in the upper right.
-
Click the Data Loss Prevention plugin.
-
Click Deploy.
-
Click Finish.
-
Click the X button in the upper-right corner of the Data Loss Prevention | Deploy dialog box.
-
Click the X button to exit the Hub.
Task 8. Create a custom template
-
In the Cloud Console, open Navigation Menu > Security > Sensitive Data Protection .
-
Click on the Configuration tab, and then click Create Template.
-
Under Define template, in the Template ID field, enter an ID for your template. You will need the template ID later in the tutorial.
-
Click Continue.
-
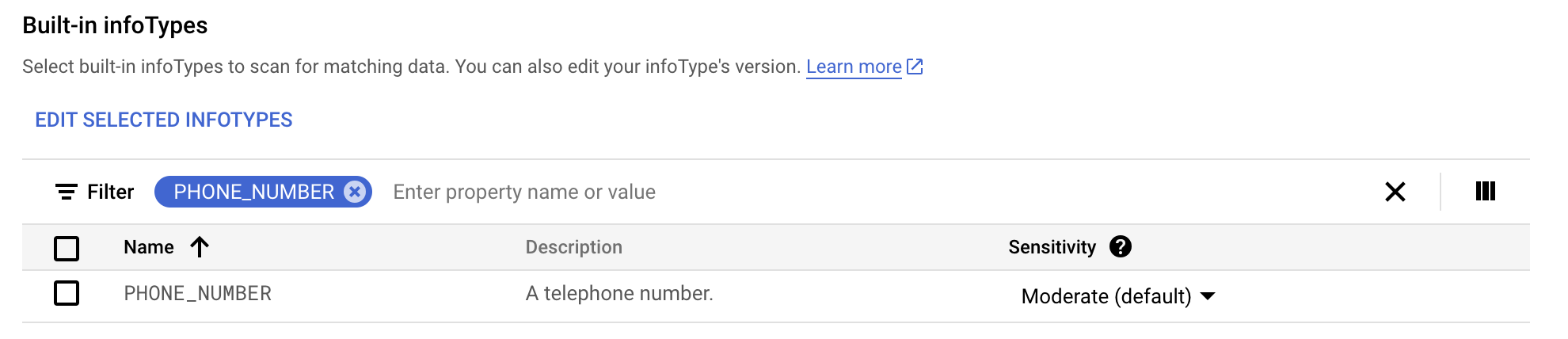
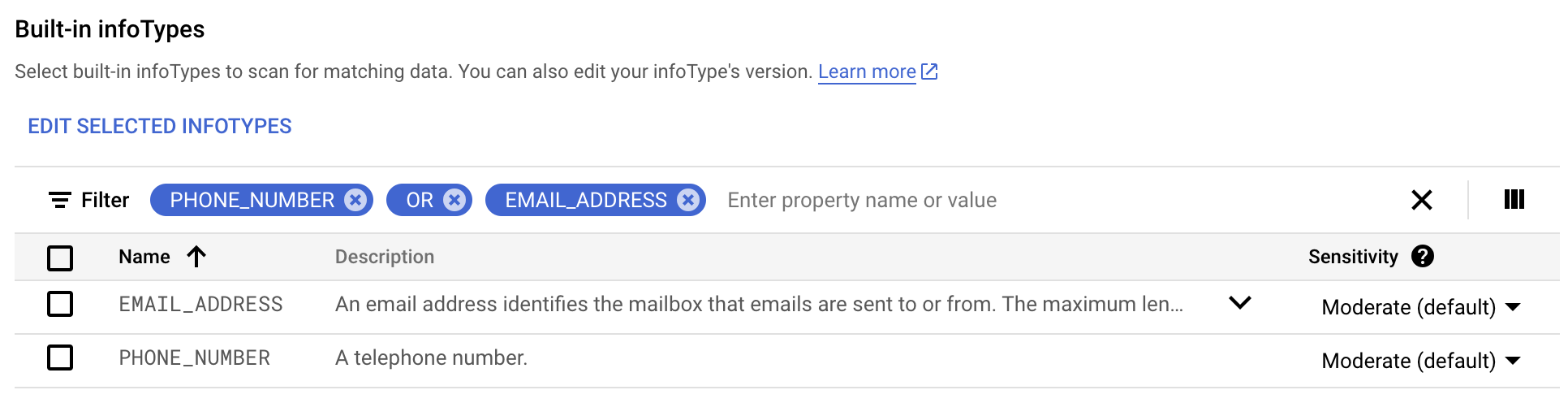
Under Configure detection, click Manage infotypes.
-
In the Built-in tab, use the filter to search for
phone number.
-
Select PHONE_NUMBER.
-
Click Done.
-
Click Create.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Task 9. Apply the Redact transform
-
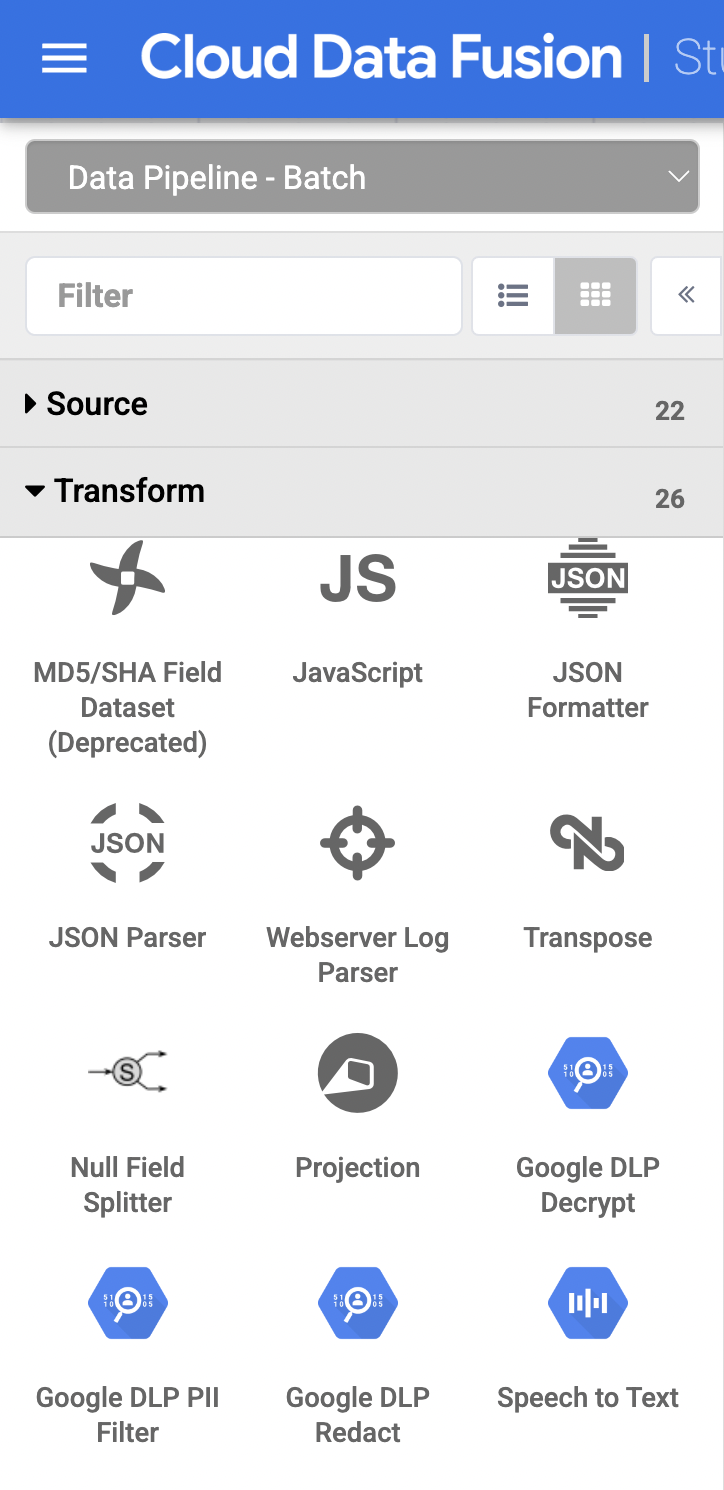
Back in the Cloud Data Fusion UI, on the Studio page, click to expand the Transform menu.
-
Click the Google DLP Redact transform plugin.
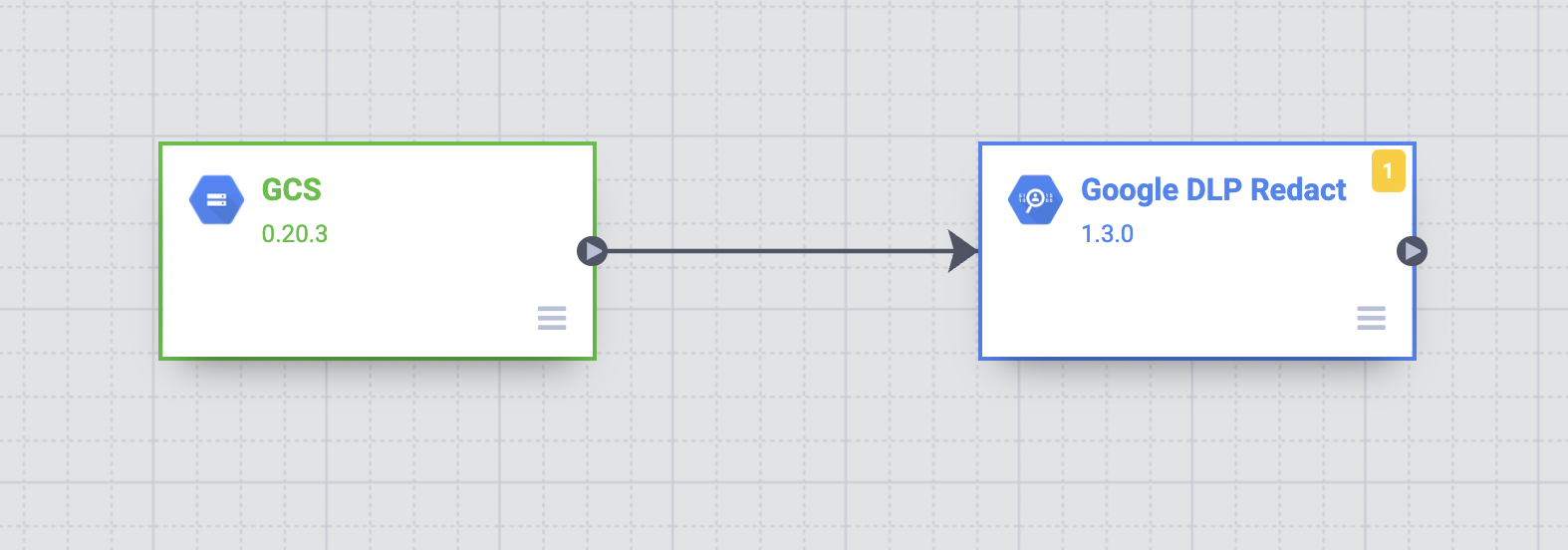
- Drag a connection arrow from the GCS node to the Google DLP Redact node.
- Hold the pointer over the Google DLP Redact node and click Properties.
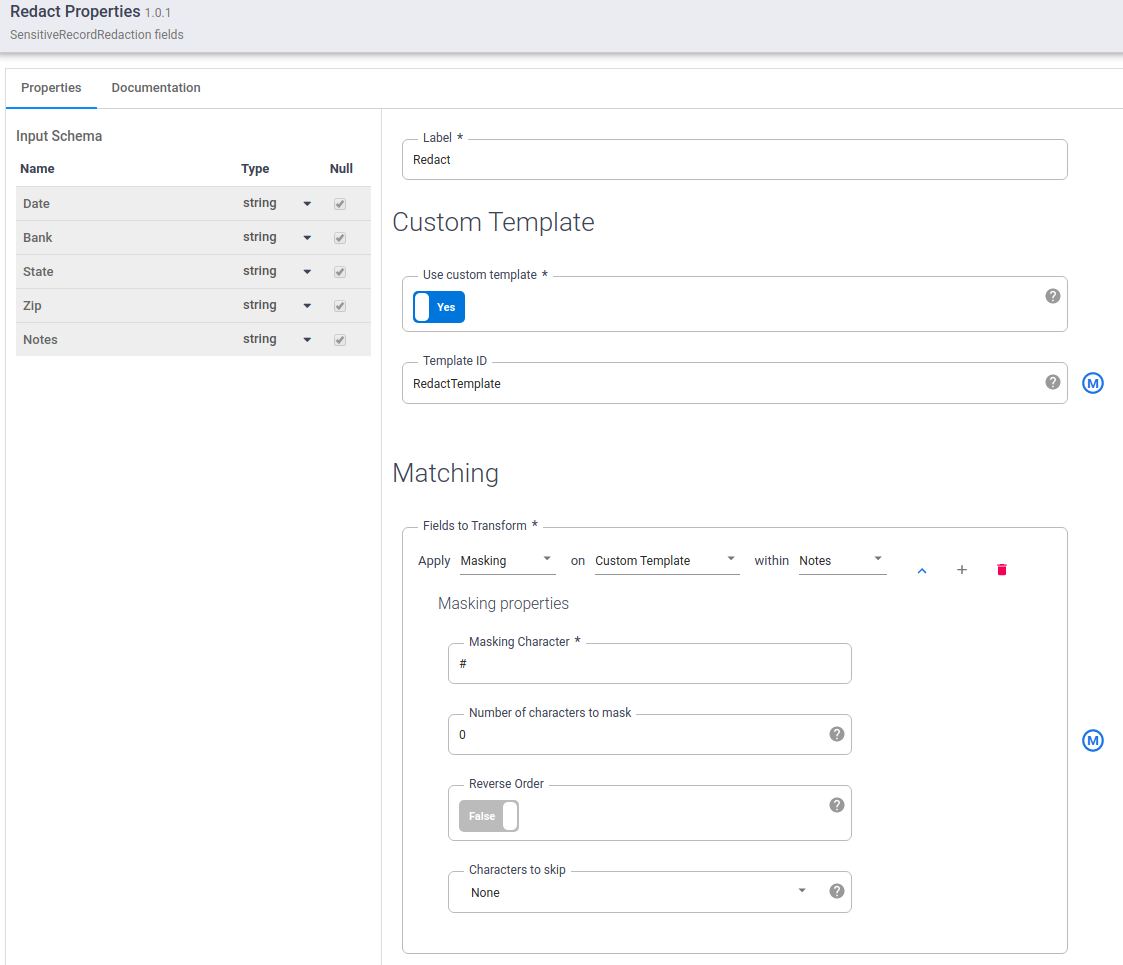
- Set Use custom template to Yes.
- Under Template ID, enter the template ID of the custom template you created.
- Under Matching, apply Masking on Custom template within Notes.
- Under Masking Character, enter
#.
-
Click Validate to ensure that there are no errors.
-
Click the X button in the upper-right corner of the dialog box.
Task 10. Store the output data
Store the results of your pipeline in a Cloud Storage file.
-
In the Cloud Data Fusion UI, on the Studio page, click to expand the Sink menu.
-
Click GCS.
-
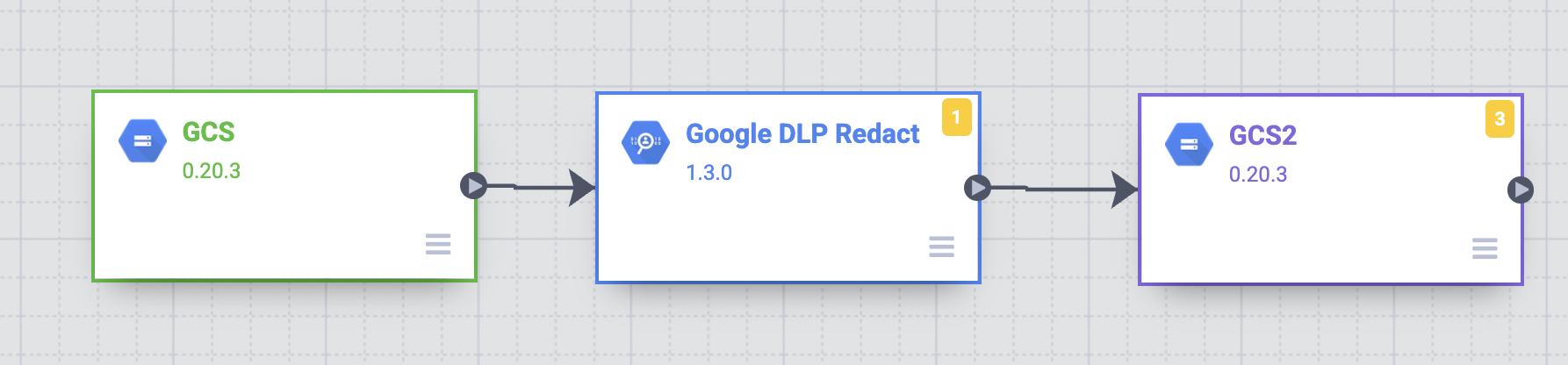
Drag a connection arrow from the Google DLP Redact node to the GCS2 node.
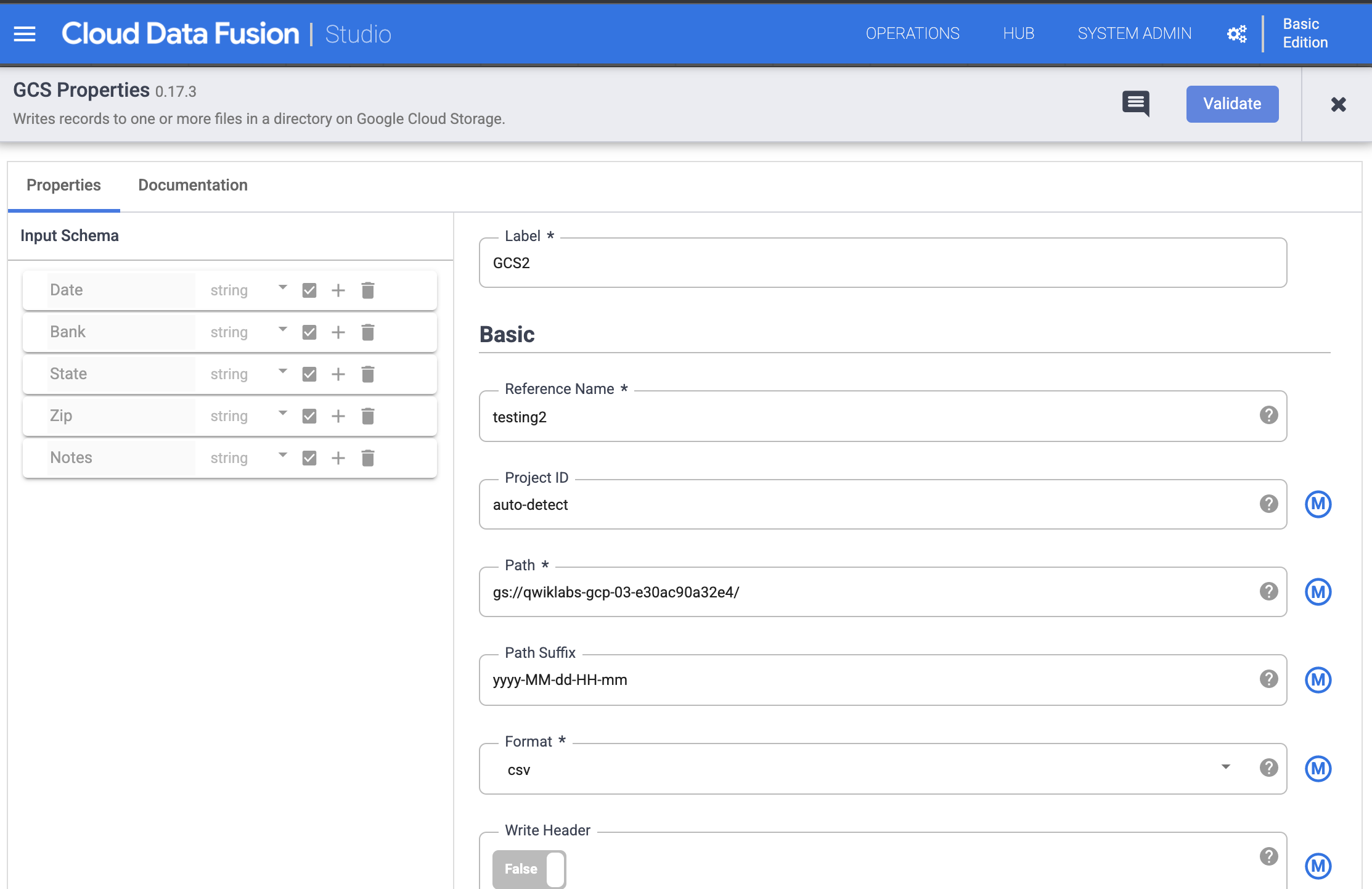
- Hold the pointer over the GCS2 node and click Properties.
- Under Reference Name, enter a reference name.
- Under Path, enter the path of the Cloud Storage bucket you created at the beginning of this lab
- Under Format, select CSV.
-
Click Validate to ensure that there are no errors.
-
Click the X button in the upper-right corner of the dialog box.
Task 11. Run the pipeline in preview mode
Next, run the pipeline in preview mode before deploying it.
- Click Preview and then click Run.
The Run button displays the pipeline status, which starts with Starting, then turns to Stop, and then turns to Run.
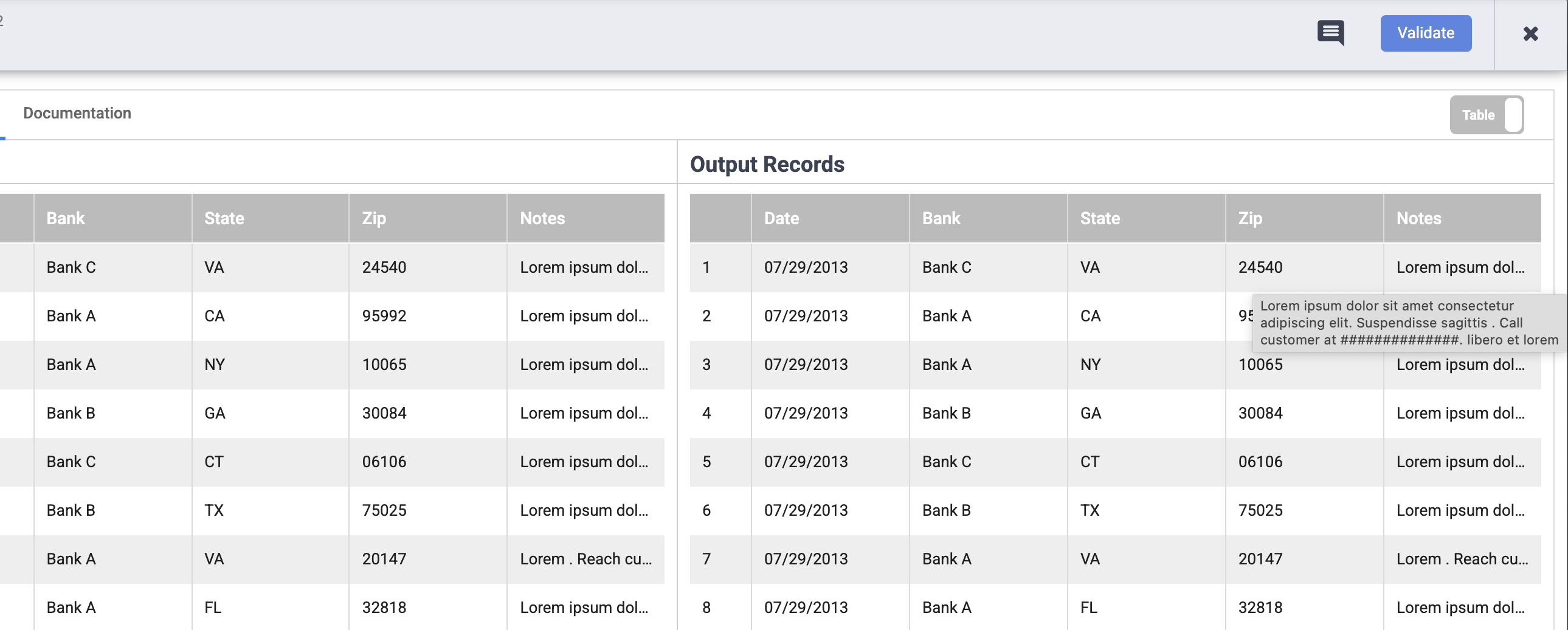
- When the preview run completes, on the Google DLP Redact node, click Preview Data to see a side-by-side comparison of the input and output data. Confirm that phone numbers have been masked with the # character.
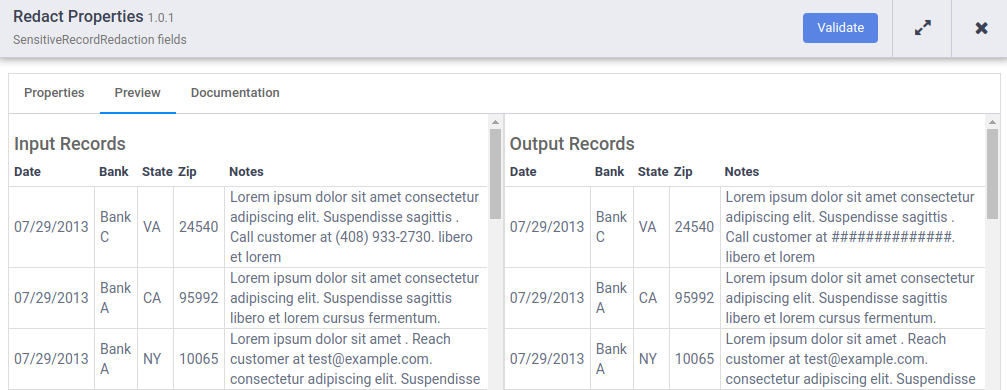
Task 12. Redact another data type
While examining the preview run results, you notice that other sensitive information appears in the Notes column: Email addresses. Go back and edit the Sensitive Data Protection inspection template to redact email addresses as well.
-
In the Cloud Console, navigate to Navigation Menu > Security > Sensitive Data Protection .
-
In the Configuration tab, select your template.
-
Click Edit.
-
Click Manage infotypes.
-
In the Built-in tab, use the filter to search for
ORemail address.
-
Select all and click Done.
-
Click Save.
-
Once again, run your pipeline in preview mode. Cloud Data Fusion will automatically use the updated Sensitive Data Protection template.
-
Confirm that both phone numbers and email addresses have been masked with the # character.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Task 13. Deploy and run the pipeline
-
Make sure Preview mode is unchecked.
-
Click Save. Clicking Save prompts you to name your pipeline. Give your pipeline a name; then click Save.
-
Click Deploy.
-
When deployment completes, click Run. Running your pipeline can take a few minutes. While you wait, you can observe the Status of the pipeline transition from Provisioning to Starting to Running to Succeeded.
Click Check my progress to verify the objective.
Task 14. View the results
-
In the Cloud Console, go to Cloud Storage.
-
In the Storage browser, navigate to the Cloud Storage bucket you specified in the sink Cloud Storage plugin properties.
-
In Authenticated URL, copy the link and paste it into a new browser tab to download the CSV file with the results. Confirm that phone numbers and email addresses have been masked with the # character.
Congratulations!
In this lab, you have learned how to use Sensitive Data Protection to mask certain parts of your data running through the Data Fusion pipeline. Ths helps when you need to remove/mask PII information embedded within your data before sharing it with your audience.
Learn more about creating Sensitive Data Protection templates by referring to the documentation.
Continue your quest
This self-paced lab is part of the Building Advanced Codeless Pipelines on Cloud Data Fusion quest. A quest is a series of related labs that form a learning path. Completing this quest earns you a badge to recognize your achievement. You can make your badge or badges public and link to them in your online resume or social media account. Enroll in this quest and get immediate completion credit. Refer to the Google Cloud Skills Boost catalog for all available quests.
Take your next lab
Continue your quest with Exploring the Lineage of Data with Cloud Data Fusion.
Manual Last Updated December 20, 2023
Lab Last Tested December 20, 2023
Copyright 2022 Google LLC All rights reserved. Google and the Google logo are trademarks of Google LLC. All other company and product names may be trademarks of the respective companies with which they are associated.